作业
1. 完成编译
2. 修改模型的大小为宽度 -90~90 km,高度为 90 km
3. 完成棋盘格模型生成正演
程序运行
编译
依次运行下列代码完成编译,最后在bin文件夹下生成需要的xspecfem2D_no_adj_snap_save和xspecfem2D_no_adj_snap_save_modify_bielak_condition_newest_bottom_absorb文件。
# specfem2D-master下编译
make clean
./configure FC=gfortran --without-mpi
make
# 配置环境
export PATH=/home/lijh/specfem2D-master/bin:$PATH >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
echo $PATH
# 正演编译
cd src/specfem2D
cp compute_Bielak_conditions_add_bottom_function_with_gaussian_STF.f90 compute_Bielak_conditions.f90
cp compute_stacey_elastic_new_modified_bottom_absorb.f90 compute_stacey_elastic.f90
cd ../..
make spec
cd bin
cp xspecfem2D xspecfem2D_no_adj_snap_save_modify_bielak_condition_newest_bottom_absorb
cd ..
# 反演编译
cd src/specfem2D
cp compute_Bielak_conditions_original.f90 compute_Bielak_conditions.f90
cp compute_stacey_elastic_original.f90 compute_stacey_elastic.f90
cd ../..
make spec
cd bin
cp xspecfem2D xspecfem2D_no_adj_snap_save
cd ..
修改模型
长度和宽度的修改在parafile文件里进行,该文件主要的参数修改如下:
MODEL =default
# first receiver set (repeat these 6 lines and adjust nreceiversets accordingly)
nrec = 121
xdeb = -60000.
zdeb = 90000.
xfin = 60000.
zfin = 90000.
record_at_surface_same_vertical = .true.
# file containing interfaces for internal mesh
interfacesfile = ../interfaces_simple_topo_sphere_90km.dat
# geometry of the model (origin lower-left corner = 0,0) and mesh description
xmin = -90000.d0
xmax = 90000.d0
nx = 90
# define the different regions of the model in the (nx,nz) spectral-element mesh
nbregions = 3
1 90 1 15 1
1 90 16 30 7
1 90 31 45 8
高度的修改在interfaces文件里进行,修改如下,修改完成后重命名为interfaces_simple_topo_sphere_90km.dat,与Par_file里的命名对应。
# number of interfaces
2
# interface number 1 (bottom of the mesh)
2
-90000 0
90000 0
# interface number 2
2
-90000 90000
90000 90000
# layer number 1 (bottom layer)
45
棋盘格测试与正演
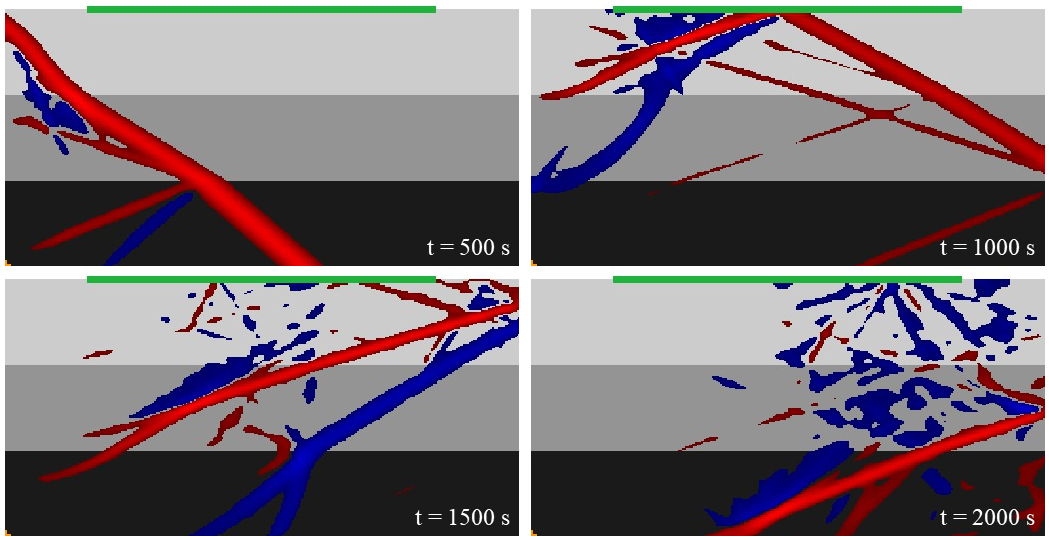
运行脚本生成一个三层的水平层状速度模型以及相应的波场快照,其中震源位于左下角,绿色部分为台站,模型颜色越深的部分速度越高。
bash run_this_example_only_forward_test_incidence_angle.sh
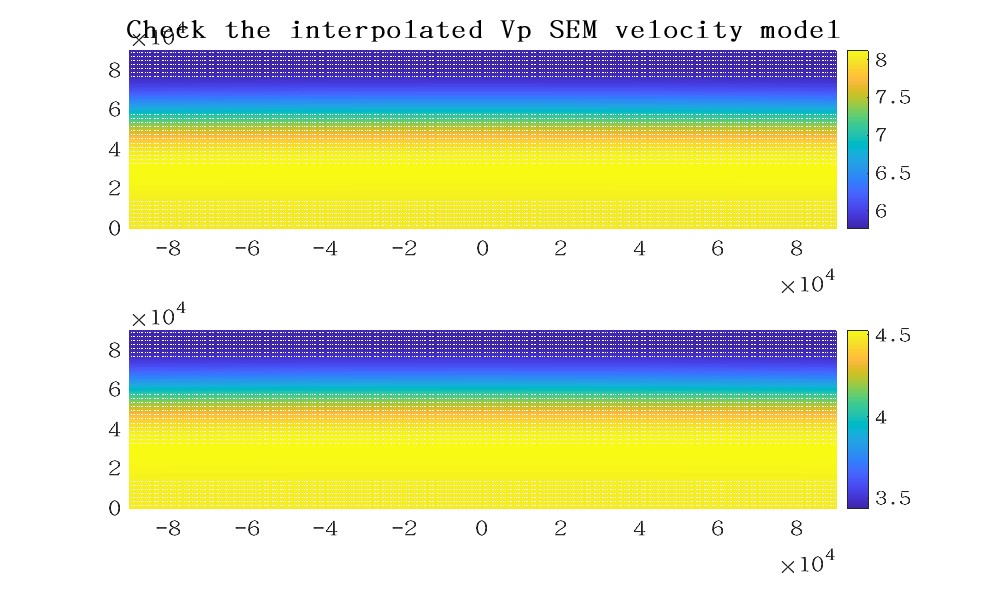
修改assign_initial_velm_model_for_spherical_topo_region.m文件里的文件路径,修改checkerboard_anomalies_generation.m里的棋盘格模型范围和格子大小如下,运行matlab脚本得到AK135模型和棋盘格测试模型。
len_z=7.5
num_z=5
len_x = 7.5
num_x = 10
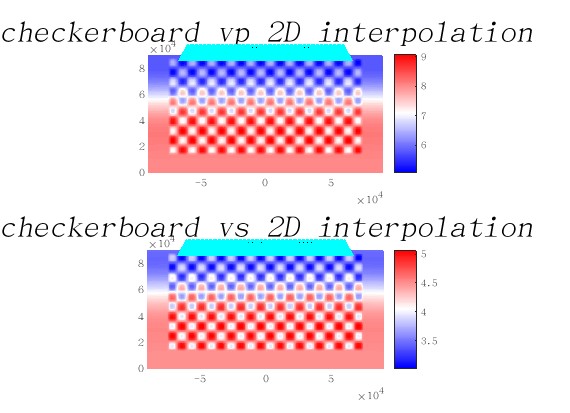
修改脚本如下使得用棋盘格模型进行正演,得到棋盘格测试结果。
cp Dingjie2_model_velocity.dat_new_defined_1D_layered_with_topo_two_layer_checkerboard_smooth_ak135_-90_to_90_ele_90_45_checkerboard proc000000_model_velocity.dat_input
收获
伴随波场反传的意义在于,它将“数据误差”的信息传递回模型中,帮助我们找到哪些区域的模型参数需要调整。通过正向波场和伴随波场的相关,我们能知道如何修改模型以减少误差,从而实现反演目标。 正向波场:从震源开始正向传播,模拟地震波的传播过程。 伴随波场:从接收点出发,利用误差作为震源,反向传播波场。 梯度计算:通过正向波场和伴随波场的相关,得到目标函数对模型参数的敏感性。
部分问题解决办法
cp compute_Bielak_conditions_add_bottom_function_with_gaussian_STF.f90 compute_Bielak_conditions.f90编译报错
解决:把compute_Bielak_conditions_add_bottom_function_with_gaussian_STF_old.f90文件的old去掉再编译。
bash run_this_example_only_forward_test_incidence_angle.sh报错
解决:docker拉取ubuntu22.04或者更新libc6。
Last modified on 2024-12-21